Russian Railway Network and Trade Data
As of 2022, Russian public railway network has a total operational mileage of 87,000 kilometers, ranking third in the world. In 2022, Russia's railway passenger volume reached 1.14 billion, up 7.9% year-on-year, while freight volume was 1.24 billion tons, down 3.7% year-on-year.
The Moscow-St. Petersburg Sapsan high-speed railway, which began operation in 2009, is Russia's first high-speed railway. It uses Siemens Velaro trains with a maximum speed of 250 km/h. The second high-speed railway, the Moscow-Kazan line, was suspended in 2019. However, the 215-kilometer Chelyabinsk-Yekaterinburg high-speed railway has been included in Russia's transport strategy plan before 2030, with construction expected to advance.
Currently, Russia has 11 international railway lines connecting with countries such as Finland, Lithuania, Ukraine, Belarus, Azerbaijan, Mongolia, China, and North Korea. These include the October Railway, North Caucasus Railway, Moscow Railway, Volga Railway, Trans-Siberian Railway, and BAM Railway.
Major Russian cities like Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Kazan have well-developed metro systems, with a total length of over 600 kilometers.
The Baikal-Amur Mainline (BAM), a 4,324-kilometer railway, crosses three time zones and six regions in Russia. It is a crucial part of Russia's railway network, serving as a gateway to Asia and linking Eastern Siberia with the Far East. Celebrating its 50th anniversary in 2024, the BAM's transport capacity has significantly increased, making Russia's Asian trade corridor more capable than its traditional European routes. This growth is due to the development of new oil fields and large reserves of natural gas, copper, gold, and other metals near China and other Asian markets, creating jobs for newcomers in Russia's European part.
The Trans-Siberian Railway, also known as the First Eurasian Continental Bridge, connects Moscow and Vladivostok, spanning 9,288 kilometers. It shortens the transport route from the Atlantic to the Pacific, making it the longest railway in the world. The Trans-Siberian Railway links Russia's European part with Siberia and the Far East. About 19.1% of the railway is in Europe and 80.9% in Asia, crossing 8 time zones, 3 regions, and 14 provinces, with branches to Mongolia, China, and North Korea. This railway not only boosts Russia's economic development and urbanization but also strengthens its ties with other countries.
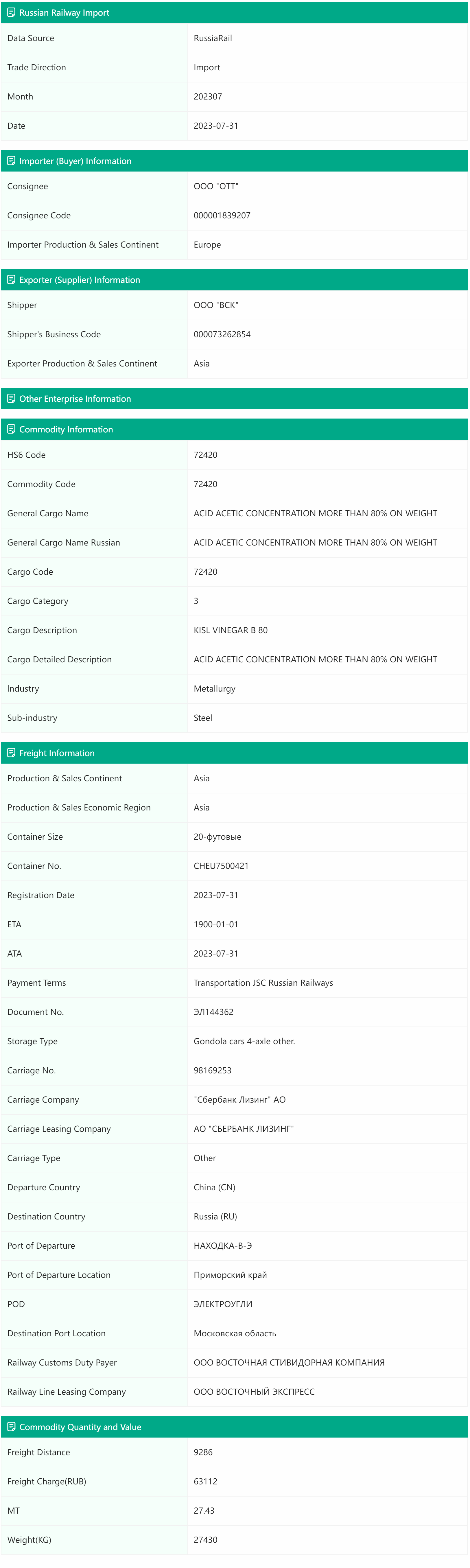
Blooming Trade Data provides comprehensive data on Russian railway transport, including import and export data, information on Russian buyers and consignees, basic cargo details (including product codes, descriptions, and categories), cargo shipment details (such as origin and destination countries, departure and arrival stations, station types, car types), as well as trade commodity weights and freight charges.
Would you like to leverage Russian railway import and export data to assess market demand, analyze competitors, and formulate trade strategies?

Sample Data