Please Sign in to view recently saved searches.
【Peru Air Transport】
Peru is located in central South America and borders the Pacific Ocean. It is a hub for air transport in South America. There are a total of 134 airports, 72 of which are civil airports. There are 11 international airports. International routes can lead to many cities in the United States, some European countries, and major Latin American countries.
The most important international airports include Jorge Chávez Airport in Lima, the capital; Arequipa; Chiclayo; Iquitos; Cusco Airport; and so on. There are 13 domestic airports, and the rest are regional airports.
The most important international airports include Jorge Chávez Airport in Lima, the capital; Arequipa; Chiclayo; Iquitos; Cusco Airport; and so on. There are 13 domestic airports, and the rest are regional airports.
At present, about 70 airports in Peru are owned by the state. Among them, 18 have been franchised to the private sector, and 29 are operated by the state-owned CORPAC company. In 2001, Jorge Chávez Airport in Lima was sold to Frankfurt Airport Management Company. The management level has been greatly improved. From 2009 to 2018, it was elected as the best airport in South America for ten consecutive years. In 2018, it ranked 49th in the world, rising by 6 places compared to 2017.
【Peru Sea Transport】
Peru borders the Pacific Ocean and has a crisscrossing network of inland rivers. The water and land transportation conditions are relatively good. There are a total of 85 ports in the country, including 58 seaports, 24 river ports, and 3 lake ports. There are a total of 103 terminals. Water transportation is relatively developed. With Peru's economy and trade growing rapidly for many consecutive years, the capacity of its existing ports is increasingly difficult to meet demand.
According to data from the Peruvian National Port Authority (APN), in 2021, the annual throughput of port terminals across the country was approximately 110 million tons, an increase of 13.7% year-on-year.
The Port of Callao adjacent to Lima, the capital, is the most important port on the Pacific coast in South America. It has been franchised to the private sector and includes three terminals: the northern, southern, and mineral terminals, which belong to APM Terminals, Dubai Ports World (DPW), and the Callao Transport Company respectively. The equipment is advanced, the management is standardized, and the degree of modernization is relatively high. In 2021, the cargo throughput of this port accounted for 70.7% of the total in Peru.
According to data from the Peruvian National Port Authority (APN), in 2021, the annual throughput of port terminals across the country was approximately 110 million tons, an increase of 13.7% year-on-year.
The Port of Callao adjacent to Lima, the capital, is the most important port on the Pacific coast in South America. It has been franchised to the private sector and includes three terminals: the northern, southern, and mineral terminals, which belong to APM Terminals, Dubai Ports World (DPW), and the Callao Transport Company respectively. The equipment is advanced, the management is standardized, and the degree of modernization is relatively high. In 2021, the cargo throughput of this port accounted for 70.7% of the total in Peru.
Other important seaports include: Paita; Bayovar; Salaverry; Chimbote; Pisco; Ilo; Matarani; and so on. Among the river ports, Iquitos is relatively important.
The total throughput of Peru's franchised ports from January to October 2023 reached 45 million tons, an increase of 3.8% year-on-year, reflecting the improvement of Peru's port operation capacity and the volume of foreign trade sea exports. 80% of Peru's foreign trade goods are exported by sea. Bulk cargo is mainly transported by the northern multi-purpose terminal at the Port of Callao, the new container terminal in the southern area, and the Matarani terminal. The transportation volumes are 14.9 million tons, 14.5 million tons, and 6.1 million tons respectively.
From January to October 2023, Peru's franchised ports transported more than 2.4 million 20-foot standard containers. The southern terminal with the largest transportation volume transported 1.3 million containers. Followed by the northern terminal with a total of 903,675 containers. The San Martín port in Pisco transported 10,274 containers. During the same period, a total of 3,571 ships passed through eight franchised ports in Peru.
From January to October 2023, Peru's franchised ports transported more than 2.4 million 20-foot standard containers. The southern terminal with the largest transportation volume transported 1.3 million containers. Followed by the northern terminal with a total of 903,675 containers. The San Martín port in Pisco transported 10,274 containers. During the same period, a total of 3,571 ships passed through eight franchised ports in Peru.
【Economic and Trade Agreements】
Peru actively participates in global multilateral and bilateral trade mechanisms to expand its foreign trade market and create a favorable trade environment. Overall, Peru's achievements in free trade agreement construction are leading globally.
According to information released by the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism of Peru, Peru has signed 27 trade agreements, of which 24 have entered into force and 3 are awaiting entry into force. In addition, seven trade agreements are under negotiation.
From January to June 2023, trade between Peru and its partners with various regional trade agreements (RTAs) accounted for 91.9% of Peru's total foreign trade.
【Multilateral Agreements】
Peru joined the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade in 1951 and became a founding member of the World Trade Organization in January 1995.
【Regional Group Agreements】
Peru participates in trade agreements of multiple regional trade groups.
Peru is a member of the Andean Community, which also includes other members such as Colombia, Bolivia, and Ecuador. Members of this regional group have signed a common tariff agreement, and Peruvian products enjoy zero-tariff access to the markets of member countries.
Peru has signed a preferential trade agreement with Mercosur. The member countries of Mercosur include Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and Paraguay.
Peru has signed economic complementarity agreements with Mexico and Chile, granting each other preferential tariff treatment.
Peru is a member of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC). Its trade with the other 20 economies in this region accounts for more than 60% of its foreign trade.
Peru is one of the founding countries of the Pacific Alliance (including Peru, Mexico, Chile, and Colombia). The alliance has signed a high-level trade agreement, which entered into force in 2015.
Peru has joined the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP).
【Bilateral Trade Agreements】
Peru has signed bilateral trade agreements with tariff entities such as the United States, Chile, Canada, Singapore, China, South Korea, Mexico, Thailand, Japan, Panama, the European Union, Costa Rica, Cuba, Venezuela, Honduras, Australia, and the United Kingdom.
In addition, Peru has initiated free trade agreement negotiations with El Salvador, Turkey, India, and Nicaragua.
【Beneficiary Country of EU Generalized System of Preferences】
Peru is a beneficiary country of the EU's tariff preference policy. According to the new Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) plan announced by the European Commission in November 2012, Peru is listed as a category III country under the GSP. These countries are selected from category II GSP countries. Upon application by the country and after the EU reviews the country's situation in terms of joining international treaties, human rights, and environmental improvement, it is listed as a GSP+ country.
From January 1, 2014 to December 31, 2023, the EU further reduces tariffs by 3.5% on imports from 40 low-income and lower-middle-income countries including Peru on the basis of the most-favored-nation tariff rate.
【Geographical Radiation】
Peru is located in central South America. Lima-Callao is a transportation hub for land, sea, and air in the Pacific coast of South America. The market radiates to countries such as Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Venezuela.
【Blooming Trade Data】
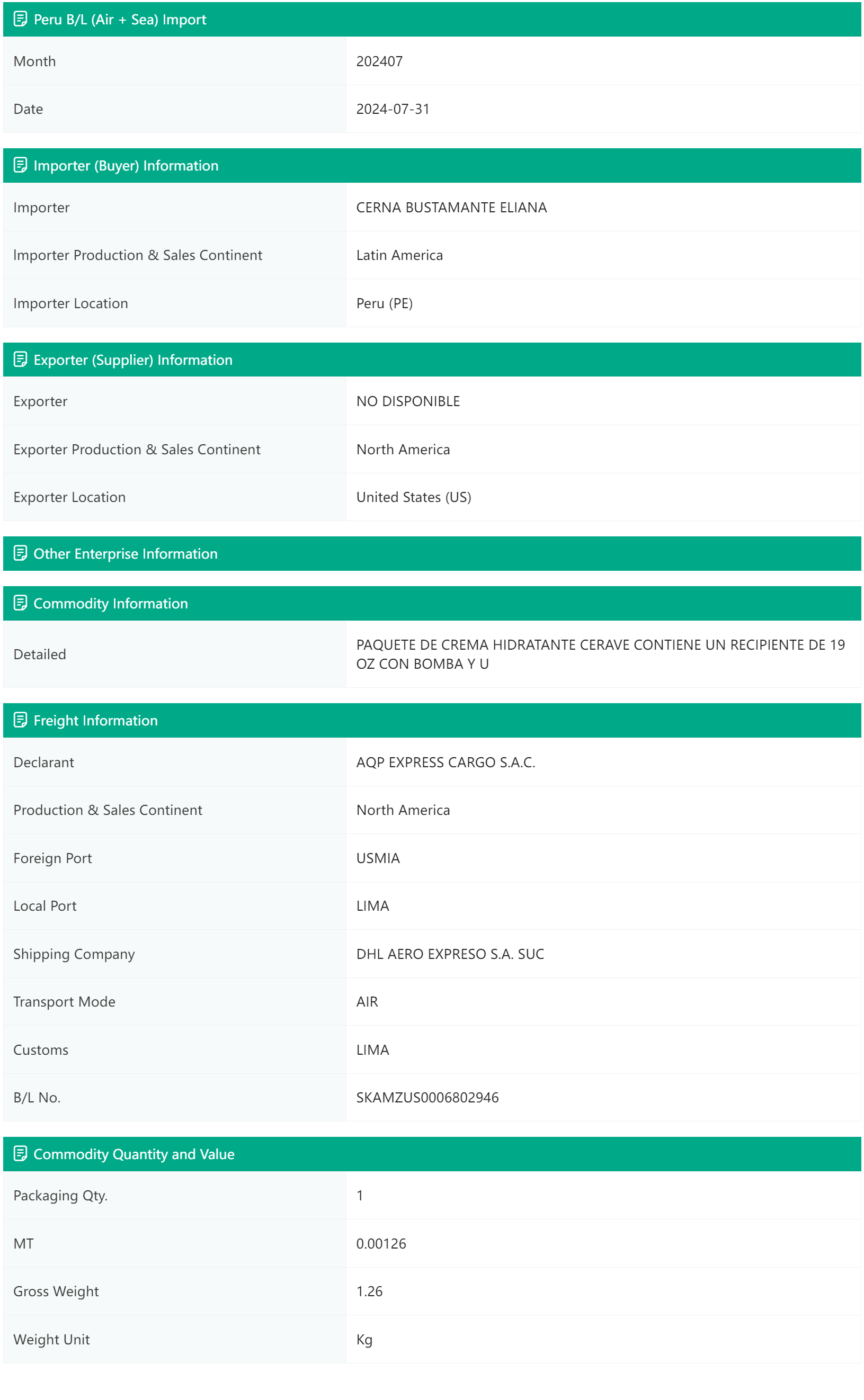
Peru bill of lading (air + sea) data is updated periodically with reliable data sources. Its transaction data includes detailed information of importers, exporter information, cargo information, freight information, and key price and volume information such as commodity trading volume, transaction amount, and transaction unit price, helping you easily grasp the latest import and export market information of air and sea transportation in Peru.
Do you want to understand the market demand in Peru? Are you looking to expand your international market presence in Peru through air and sea transportation? Are you seeking more cooperation with clients and reliable suppliers in Peru?

Sample Data

Are you interested in the activities of your competitors in the Peruvian market through air and sea transportation?
