Please Sign in to view recently saved searches.
Afghanistan is a landlocked country in central and western Asia, located at the intersection of Central Asia, West Asia, and South Asia. It borders China to the northeast, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north, Iran to the west, and Pakistan to the south and east. It has a land area of 647,500 square kilometers and a population of about 32.2 million.
Afghanistan is rich in mineral resources. According to the Afghan government's estimate, the country’s energy and mineral resources are worth over $3 trillion. More than 1,400 mineral deposits have been discovered, including iron, chromium iron, copper, lead, zinc, nickel, lithium, beryllium, gold, silver, platinum, palladium, talc, marble, barite, precious and semi-precious stones, salt, coal, and uranium.
Key Industries
Agriculture and Animal Husbandry:
Agriculture and animal husbandry are the main pillars of Afghanistan's national economy, with 85% of the population involved in these sectors. Despite this, food production is insufficient to meet domestic needs, requiring international aid or imports each year. Due to its natural geographical conditions, large farms are almost non-existent. Main crops include wheat, barley, rice, corn, cotton, dried fruits, and various fruits. Animal husbandry includes sheep, goats, cattle, and poultry, and is mostly free-range.
Afghanistan's saffron is well-known and has won multiple awards in international competitions. Recently, Afghanistan has aimed to make saffron a key export agricultural product, potentially replacing lapis lazuli as a state gift.
Industry:
Years of war have almost collapsed Afghanistan's industrial base. The country lacks a complete industrial system, and industrial output accounts for only about 25% of GDP. The industry is dominated by light industry and handicrafts, including chemicals, building materials, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, printing, food, textiles, leather, carpets, and agricultural product processing. There are no large enterprises, only small and medium-sized enterprises.
Carpet Industry:
Afghanistan's handmade carpets have a long history and are its main export products, having won awards at international exhibitions multiple times. At its peak, Afghanistan had about 1 million carpet workshops employing over 6 million people.
Energy and Mining Industry:
Afghanistan has rich energy and mineral resources and views this sector as a strategic industry. However, due to years of conflict, the energy and mining industry is currently limited to small-scale "individual" development activities, contributing minimally to GDP.
Trade Relations
Regional Cooperation:
Afghanistan participates in several regional cooperation organizations, including the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA), the Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO), the Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation Program (CAREC), and the Central and South Asian Transport and Trade Forum. In December 2015, Afghanistan joined the World Trade Organization (WTO), becoming the 164th member economy and the 36th least developed member.
Total Trade:
Afghanistan has experienced prolonged conflict, destroying many factories and leaving mineral deposits undeveloped. The country has a significant trade deficit, with annual exports of about $800 million, accounting for only 10% of total trade. Main exports include handmade carpets, dried fruits, fruits, medicinal materials, cotton, and marble.
Import Trade:
The reconstruction process has driven rapid growth in import trade. Afghanistan's weak processing and manufacturing base means the domestic market heavily relies on imports, from daily necessities to industrial and mining equipment. Main imports include household goods, medicines, food, and petroleum products.
Export Trade:
Afghanistan's export trade has shown steady growth, increasing from $376 million in the 2011/12 fiscal year to $864 million in the 2019/20 fiscal year. Main exports are carpets, dried fruits, herbs, fruits, and wool.
Trading Partners:
Afghanistan’s main trading partners are its neighbors. Iran, China, and Pakistan are major sources of imports, with imports in the 2019/20 fiscal year amounting to $1.247 billion, $1.157 billion, and $1.058 billion respectively. Pakistan and India are the main export destinations, with exports of $298 million and $410 million respectively. In 2019/20, Afghanistan had 11 countries with exports exceeding $1 million and 12 countries with imports exceeding $100 million.
Import Declarations:
According to Afghan Customs Law, the following information is required for import declarations: business license of the import unit, sales invoice of the export company, border customs trade operation form, transport bill of lading, transit bill and insurance policy, and packing list. Land transport goods require a certificate of origin. Goods exported from China to Afghanistan need a Chinese commodity inspection report as required.
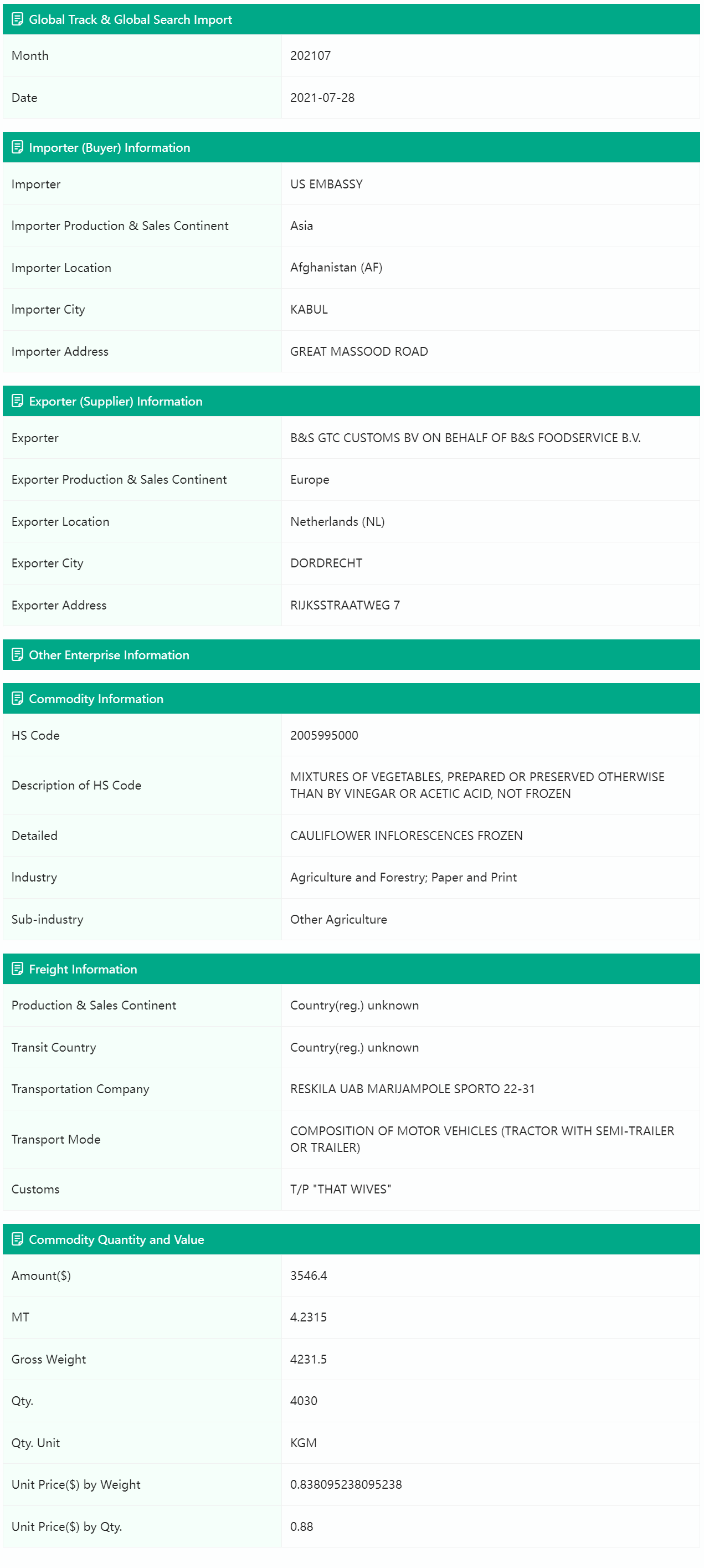
The Blooming Afghanistan B/L data includes buyer and supplier data, commodity information, transportation details, transaction prices, volumes, and amounts, helping you conduct in-depth research and make prudent business decisions in Afghanistan.
Are you looking to understand market demand in Afghanistan? Do you have aspirations to expand your business into the Afghanistan market? Are you interested in pursuing greater collaboration with clients and dependable suppliers based in Afghanistan?

Sample Data