Please Sign in to view recently saved searches.
The Philippines boasts an abundance of mineral resources, including oil, copper, gold, silver, iron, chrome, and nickel, as well as a human resource pool of over 100 million people. In 2023, the country's export volume surpassed 10 billion US dollars, setting a new record for the Philippines' foreign trade income and positioning it as one of the fastest-growing economies in the East Asia and Pacific region.
As a significant electronics production and export hub in Southeast Asia, the Philippines sees brisk foreign trade in electronic products and components, ranging from smartphones and tablets to various electronic accessories. Leveraging a robust supply chain, labor force advantages, and supportive policies, these products are highly competitive in the global market.
Known for its diverse and flavorful agricultural products and cuisine, the Philippines enjoys popularity for its tropical fruits such as coconuts, bananas, and pineapples, as well as high-quality rice and seafood in international markets.
The Philippines also prides itself on its unique and rich culture, with its handicrafts and creative products standing out in the global market. From exquisite wooden furniture and hand-woven items to distinctive ethnic attire, the creative industries in the Philippines are emerging as a new growth driver for foreign trade.
Manila Port, Cebu Port, and Davao Port are the three major ports in the Philippines.
Manila Port, with its extensive international routes, maintains direct connections with major ports such as Hong Kong, Shanghai, Yokohama in Japan, and Singapore.
Cebu Port, equipped with 20 principal berths and a shoreline of 3,303 meters with a maximum depth of 12 meters, primarily exports coconut oil, copra, hemp, tobacco leaves, timber, cement, mineral sand, and sugar, while importing coal, petroleum, wheat, rice, salt, hardware products, and groceries.
Davao Port, the largest port and economic center in southern Mindanao, is also the national center for abaca processing.
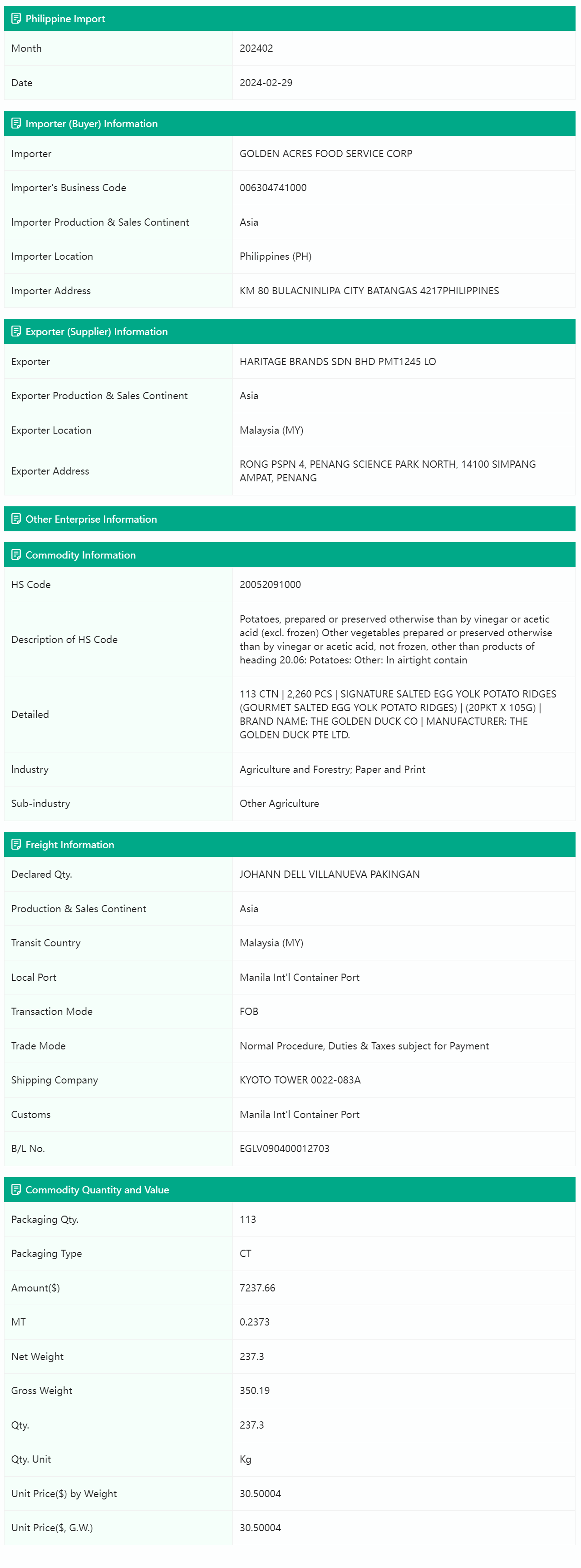
Philippine customs data includes:
1) the names of importers and exporters, aiding in the identification of trade partners and market participants;
2) specific product descriptions and 10-digit customs codes for the classification and analysis of import and export goods;
3) details such as weight, quantity, FOB (Free On Board), and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) values, which are crucial for assessing market size and product value;
4) the origin and destination countries of imports and exports, providing insights into the Philippines' trade partners and market distribution.
1) the names of importers and exporters, aiding in the identification of trade partners and market participants;
2) specific product descriptions and 10-digit customs codes for the classification and analysis of import and export goods;
3) details such as weight, quantity, FOB (Free On Board), and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) values, which are crucial for assessing market size and product value;
4) the origin and destination countries of imports and exports, providing insights into the Philippines' trade partners and market distribution.
By analyzing customs data, businesses can gain insights into the demand and supply situation in the Philippine market, as well as potential growth areas. The data can also be used to identify competitors and analyze the Philippine market share and trade strategies.
Are you interested in understanding the market demand in the Philippines? Are you seeking to expand your international market presence in the Philippines? Are you looking to establish more cooperation with clients and reliable suppliers in the Philippines?

Sample Data